(Peer-Reviewed) Reducing loss of significance in the computation of Earth-based two-way Doppler observables for small body missions
Wei-Tong Jin 金炜桐 ¹ ², Fei Li 李斐 ¹ ³, Jian-Guo Yan 鄢建国 ¹, Xuan Yang 杨轩 ¹ ², Mao Ye 叶茂 ¹, Wei-Feng Hao 郝卫锋 ³, Thomas Paul Andert ⁴, Jean-Pierre Barriot ⁵
¹ State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, China
中国 武汉 武汉大学测绘遥感信息工程国家重点实验室
² State Key Laboratory of Satellite Navigation System and Equipment Technology, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
中国 石家庄 卫星导航系统与装备技术国家重点实验室
³ Chinese Antarctic Center of Surveying and Mapping, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, China
中国 武汉 武汉大学中国南极测绘研究中心
⁴ Universitat der Bundeswehr München, Neubiberg, Bayern, 85579, Germany
⁵ University of French Polynesia, BP 6570, F-98702 Faa'a, Tahiti, French Polynesia
Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics (RAA), 2021-03-19
Abstract
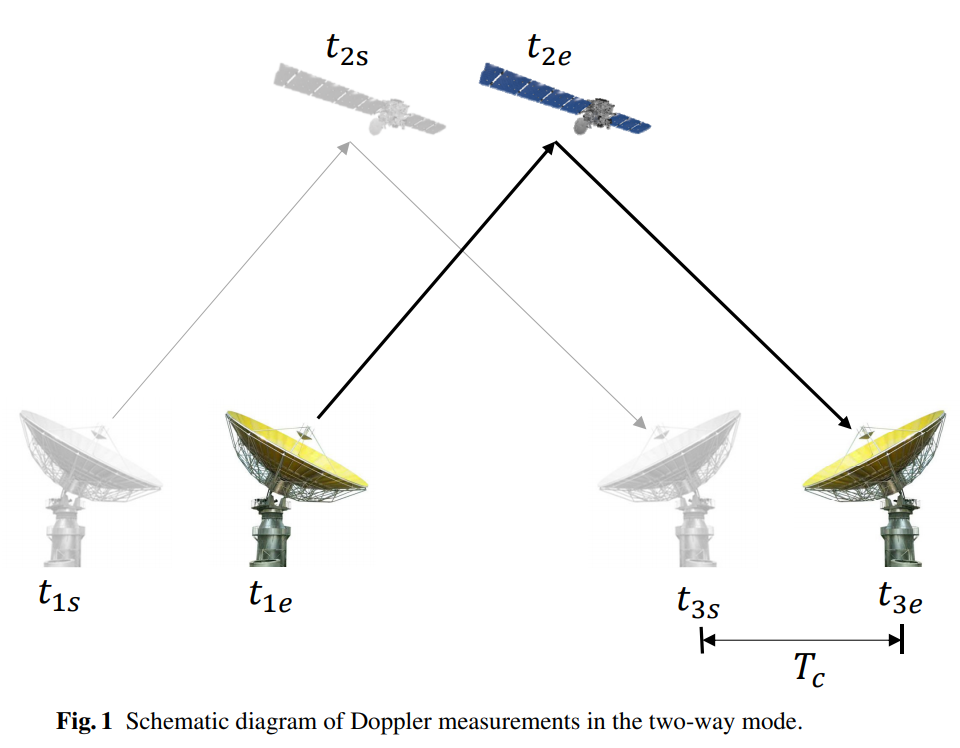
Two-way Doppler measurement is a typical Earth-based radiometric technique for interplanetary spacecraft navigation and gravity science investigation. The most widely used model for the computation of two-way Doppler observables is Moyer’s differenced-range Doppler (DRD) formula, which is based on a Schwarzschild approximation of the Solar-System space-time.
However, the computation of range difference in DRD formula is sensitive to round-off errors due to approximate numbers defined by the norm IEEE754 in all PCs. This paper presented two updated models and their corresponding detailed instructions for the computation of the two-way Doppler observables so as to impair the effects of this type of numerical error. These two models were validated by two case studies related to the Rosetta mission—asteroid Lutetia flyby and comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko orbiting case. In these two cases, the numerical noise from the updated models can be reduced by two orders-of-magnitude in the computed two-way Doppler observables. The results showed an accuracy from better than 6×10⁻³ mm s⁻¹ at 1 s counting time interval to better than 3 × 10⁻⁵ mm s⁻¹ at 60 s counting time interval.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25