(Peer-Reviewed) Flat multifunctional liquid crystal elements through multi-dimensional information multiplexing
Dongliang Tang 汤东亮 ¹, Zhenglong Shao 邵正龙 ¹, Xin Xie 谢鑫 ², Yingjie Zhou 周英杰 ¹, Xiaohu Zhang 张晓虎 ³, Fan Fan 樊帆 ¹, Shuangchun Wen 文双春 ¹
¹ Key Laboratory for Micro/Nano Optoelectronic Devices of Ministry of Education & Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Structural Physics and Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
中国 长沙 湖南大学物理与微电子科学学院 低维结构物理与器件湖南省重点实验室 微纳光电器件及应用教育部重点实验室
² Key Laboratory of Light Field Manipulation and Information Acquisition, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Physical Science and Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710129, China
中国 西安 西北工业大学物理科学与技术学院, 陕西省光信息技术重点实验室 光场调控与信息感知工业和信息化部重点实验室
³ Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology and Systems of the Education Ministry of China, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
中国 重庆 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-10-28
Abstract
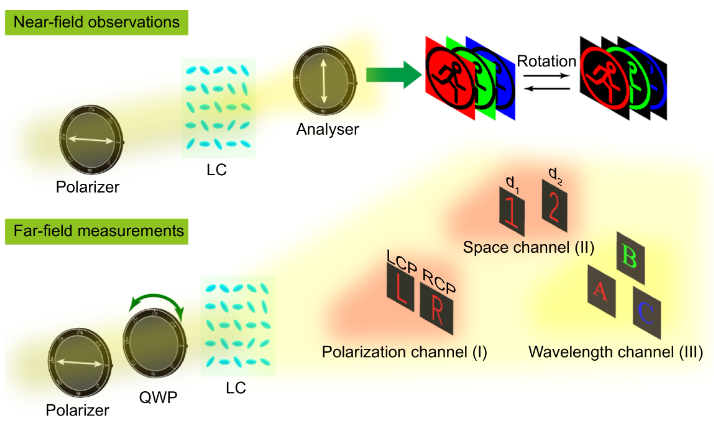
Flat optical elements have attracted enormous attentions and act as promising candidates for the next generation of optical components. As one of the most outstanding representatives, liquid crystal (LC) has been widely applied in flat panel display industries and inspires the wavefront modulation with the development of LC alignment techniques. However, most LC elements perform only one type of optical manipulation and are difficult to realize the multifunctionality and light integration.
Here, flat multifunctional liquid crystal elements (FMLCEs), merely composed of anisotropic LC molecules with space-variant orientations, are presented for multichannel information manipulation by means of polarization, space and wavelength multiplexing. Specifically, benefiting from the unique light response with the change of the incident polarization, observation plane, and working wavelength, a series of FMLCEs are demonstrated to achieve distinct near- and far-field display functions.
The proposed strategy takes full advantage of basic optical parameters as the decrypted keys to improve the information capacity and security, and we expect it to find potential applications in information encryption, optical anti-counterfeiting, virtual/augmented reality, etc.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25