(Peer-Reviewed) Applying nanotechnology to boost cancer immunotherapy by promoting immunogenic cell death
Lvqin Fu ¹, Xianbin Ma ², Yuantong Liu ¹, Zhigang Xu 许志刚 ², Zhijun Sun 孙志军 ¹
¹ The State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Basic Science of Stomatology (Hubei- MOST) & Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine Ministry of Education, School & Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, China
中国 武汉 武汉大学口腔医学院 口腔基础医学重点实验室(湖北省科技厅) 口腔生物医学教育部重点实验室
² Key Laboratory of Luminescence Analysis and Molecular Sensing (Southwest University), Ministry of Education, School of Materials and Energy & Chongqing Engineering Research Center for Micro-Nano Biomedical Materials and Devices, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
中国 重庆 发光与实时分析化学教育部重点实验室 (西南大学) 材料与能源学院 重庆市微纳生物医用材料及器件工程技术研究中心
Abstract
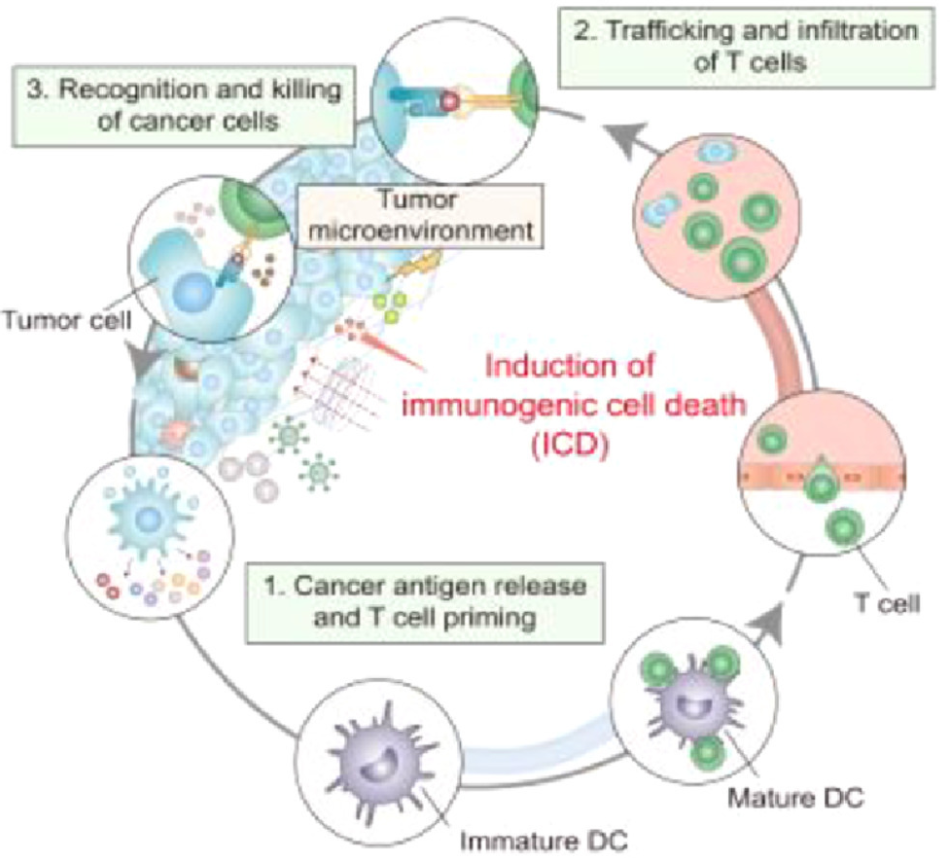
Tumor immunotherapy, especially immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), has revolutionized the cancer field. However, the limited response of tumors to immunotherapy is a major obstacle. Tumor immunogenic cell death (ICD) is a death mode of tumor cells that can promote tumor immunity.
ICD can induce strong antitumor immune responses through the ectopic exposure of calreticulin on the plasma membrane surface and the release of the non-histone nuclear protein high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), ATP, and interferon (IFN), thus activating an adaptive immune response against dead cell-associated antigens and enhancing the therapeutic effect of tumor immunotherapy. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, photothermal therapy, magneto-thermodynamics therapy, nanopulse stimulation, and oncolytic virus therapy can all induce a strong antitumor immune response by ICD.
In addition, the application of nanotechnology can precisely target drug delivery and improve the efficacy of immunotherapy. Here we introduce the basic concepts and molecular mechanisms underlying the induction of ICD. Then, we summarize and discuss the progress in the application of nanotechnology in immunotherapy to promote ICD.
Finally, we attempt to define the challenges and future directions in this area to extend the benefits of ICD to a broader patient population.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25