(Peer-Reviewed) Third-harmonic generation and imaging with resonant Si membrane metasurface
Ze Zheng ¹, Lei Xu 徐雷 ¹, Lujun Huang 黄陆军 ² ³, Daria Smirnova ⁴, Khosro Zangeneh Kamali ⁴, Arman Yousefi ¹, Fu Deng ⁵, Rocio Camacho-Morales ⁴, Cuifeng Ying ¹, Andrey E. Miroshnichenko ², Dragomir N. Neshev ⁴, Mohsen Rahmani ¹
¹ Advanced Optics and Photonics Laboratory, Department of Engineering, School of Science & Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham NG11 8NS, UK
² School of Engineering and Information Technology, University of New South Wales, Canberra ACT 2600, Australia
³ School of Physics and Electronic Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
中国 上海 华东师范大学物理与电子科学学院
⁴ ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems (TMOS), Research School of Physics, Australian National University, Canberra ACT 2601, Australia
⁵ Department of Physics, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China
中国 香港 香港科技大学物理系
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2023-08-31
Abstract
Dielectric metasurfaces play an increasingly important role in enhancing optical nonlinear generations owing to their ability to support strong light-matter interactions based on Mie-type multipolar resonances. Compared to metasurfaces composed of the periodic arrangement of nanoparticles, inverse, so-called, membrane metasurfaces offer unique possibilities for supporting multipolar resonances, while maintaining small unit cell size, large mode volume and high field enhancement for enhancing nonlinear frequency conversion.
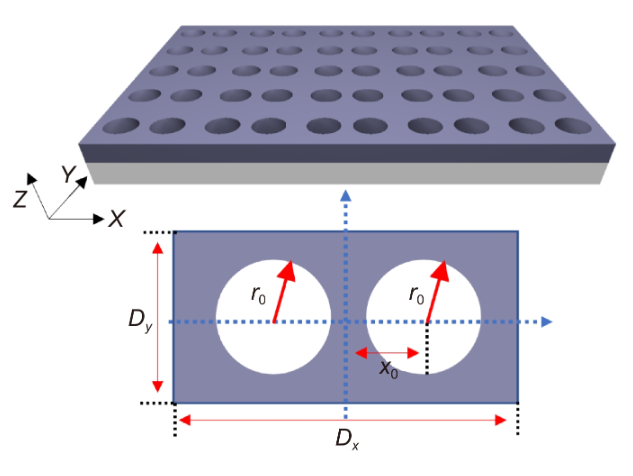
Here, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the formation of bound states in the continuum (BICs) from silicon dimer-hole membrane metasurfaces. We demonstrate that our BIC-formed resonance features a strong and tailorable electric near-field confinement inside the silicon membrane films. Furthermore, we show that by tuning the gap between the holes, one can open a leaky channel to transform these regular BICs into quasi-BICs, which can be excited directly under normal plane wave incidence.
To prove the capabilities of such metasurfaces, we demonstrate the conversion of an infrared image to the visible range, based on the Third-harmonic generation (THG) process with the resonant membrane metasurfaces. Our results suggest a new paradigm for realising efficient nonlinear photonics metadevices and hold promise for extending the applications of nonlinear structuring surfaces to new types of all-optical near-infrared imaging technologies.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25