(Peer-Reviewed) Generation of structured light beams with polarization variation along arbitrary spatial trajectories using tri-layer metasurfaces
Tong Nan 南通 ¹ ², Huan Zhao 赵欢 ³, Jinying Guo 郭劲英 ⁴ ⁵, Xinke Wang 王新柯 ², Hao Tian 田浩 ¹, Yan Zhang 张岩 ²
¹ School of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学物理学院
² Beijing Key Laboratory of Metamaterials and Devices, Key Laboratory of Terahertz Optoelectronics, Ministry of Education, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Imaging Theory and Technology, Department of Physics, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100048, China
中国 北京 首都师范大学物理系 北京成像技术高精尖创新中心 太赫兹光电子学教育部重点实验室 超材料与器件北京市重点实验室
³ Institute of Microelectronics Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
中国 北京 中国科学院微电子研究所
⁴ Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
中国 上海 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所
⁵ Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电技术学院
Opto-Electronic Science
, 2024-05-28
Abstract
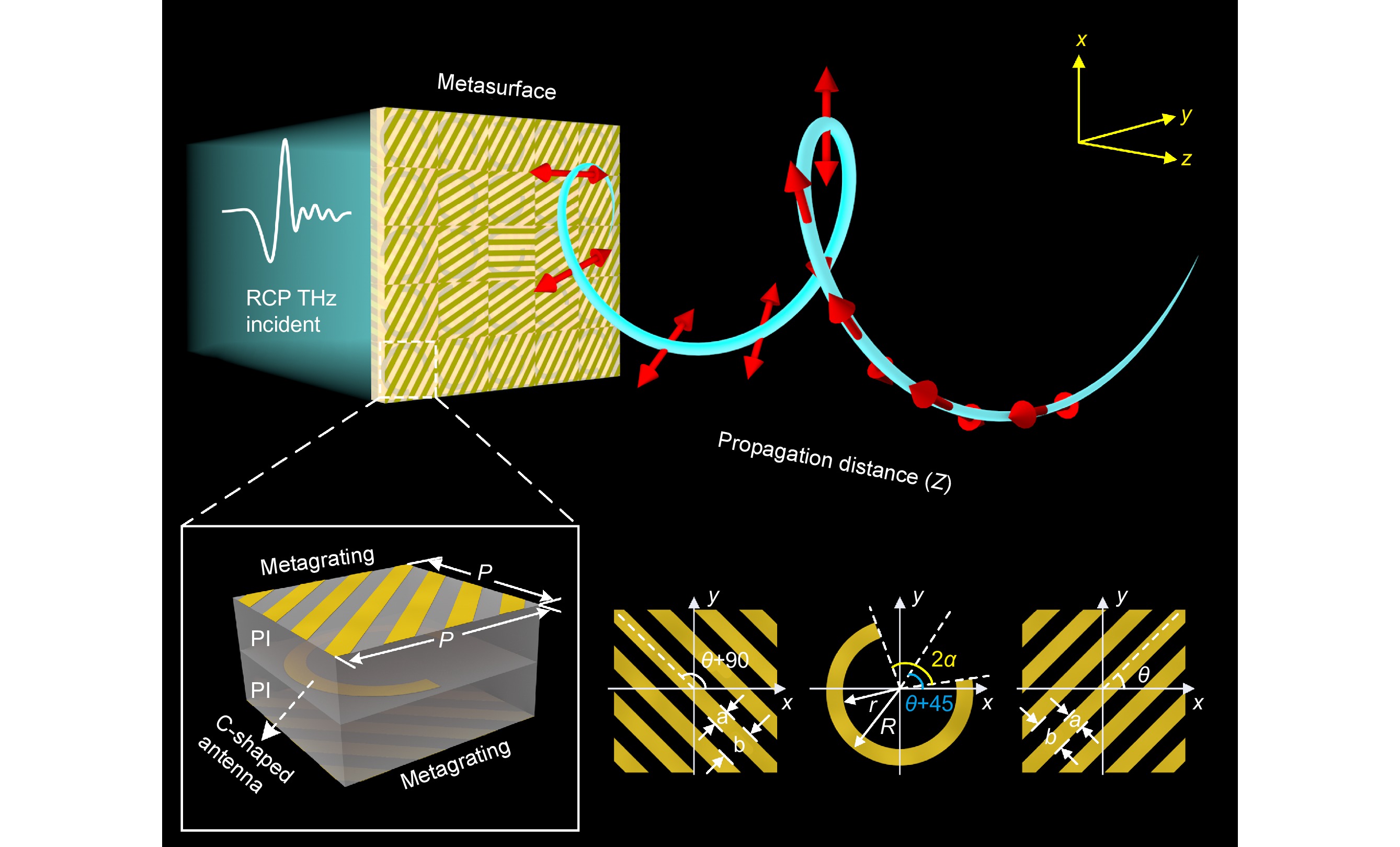
Conventionally, the spatially structured light beams produced by metasurfaces primarily highlight the polarization modulation of the beams propagating along the optical axis or the beams' spatial transmission trajectory. In particular, along the optical axis, the polarization state is either constant or varies continuously in each output plane. Here, we develop innovative spatially structured light beams with continually changing polarization along any arbitrary spatial transmission trajectories.
With tri-layer metallic metasurfaces, the geometric characteristics of each layer structure can be adjusted to modulate the phase and polarization state of the incident terahertz (THz) wave. The beam will converge to the predefined trajectory along several paths to generate a Bessel-like beam with longitudinal polarization changes. We demonstrate the versatility of the approach by designing two THz-band structured light beams with varying polarization states along the spatial helical transmission trajectory. Continuous linear polarization changes and linear polarization to right circular polarization (RCP) and back to linear polarization changes are realized respectively.
The experimental results are basically consistent with the simulated results. Our proposal for arbitrary trajectory structured light beams with longitudinally varying polarization offers a practical method for continuously regulating the characteristics of spatial structured light beams with non-axial transmission. This technique has potential uses in optical encryption, particle manipulation, and biomedical imaging.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25