(Peer-Reviewed) Halide perovskite volatile unipolar nanomemristor
Abolfazl Mahmoodpoor ¹ ², Prokhor A. Alekseev ² ³, Ksenia A. Gasnikova ² ³, Kuzmenko Natalia ⁴, Artem Larin ², Sergey Makarov ¹ ², Aleksandra Furasova ¹ ²
¹ Qingdao Innovation and Development Center, Harbin Engineering University, Qingdao 266000, China
中国 青岛 哈尔滨工程大学青岛创新发展基地
² ITMO University, School of Physics and Engineering, Kronverkskiy pr. 49, 197101, St. Petersburg, Russia
³ Ioffe Institute, 194021 Polytechnicheskaya 26, St. Petersburg, Russia
⁴ ITMO University, Research Center for Optical Materials Science, Kronverkskiy pr. 49, 197101, St. Petersburg, Russia
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2025-10-15
Abstract
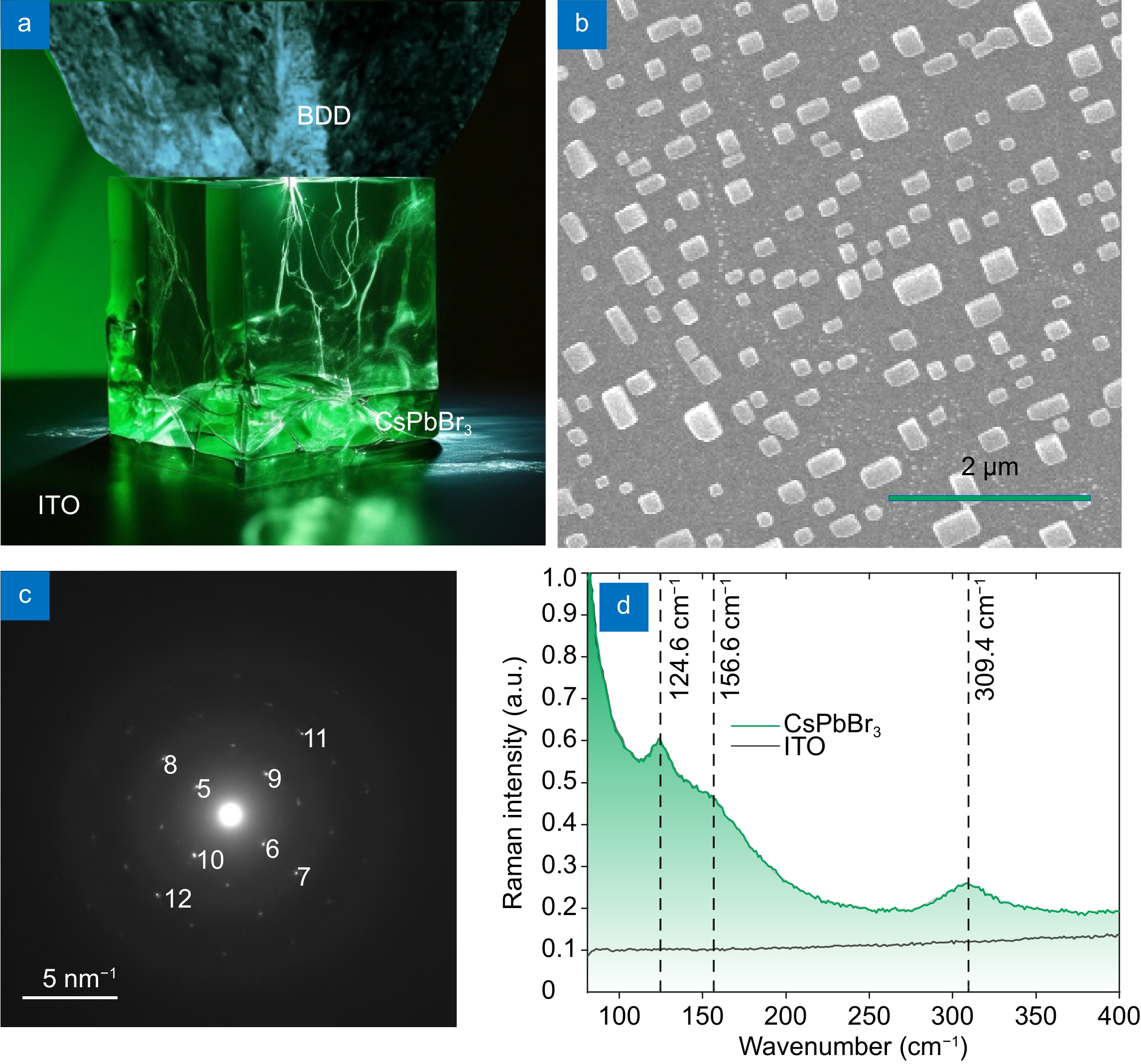
Halide perovskites is a recently emerged platform for the creation of efficient memristors. In turn, single-crystal inorganic perovskite would be new low-cost and flexible memory devices because of their excellent resistive switching (RS) properties, without risk of chemical and mechanical stress-generated degradation, compared with the operational instability of general thin-film perovskite memristors.
Moreover, miniaturization of perovskite memristors would be useful for creating high-density memory devices. Here we demonstrate the smallest CsPbBr3 perovskite nanomemristor with volatile unipolar RS characteristics which depends on the size of a single-crystal as a resistive layer due to its overall structural stability and low sensitivity to atmosphere conditions that helps to keep the stable RS switching over 1500 times with the lowest consumption power of 70 nW.
To better understand the RS mechanism, we provide a comprehensive simulation of the evolution of mixed ionic-electronic charge carriers under current-voltage (I-V) tests using a one-dimensional drift-diffusion model. Because of the nonreactive nature of the contacts, the main mechanism of resistive state switching is potential barrier modulation of the Schottky contacts through the accumulation of migrating ions at the interfaces. Our findings pave the way for ultracompact memristors as well as shed light on RS mechanism in non-filamentary perovskite-based memory devices.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Meta-lens digital image correlation
Zhou Zhao, Xiaoyuan Liu, Yu Ji, Yukun Zhang, Yong Chen, Zhendong Luo, Yuzhou Song, Zihan Geng, Takuo Tanaka, Fei Qi, Shengxian Shi, Mu Ku Chen
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-29