(Peer-Reviewed) Disordered Translocation is Hastening Local Extinction of the Chinese Giant Salamander
Guocheng SHU ¹ ², Ping LIU ¹ ³, Tian ZHAO ¹, Cheng LI 李成 ¹ ³, Yinmeng HOU ¹ ⁴, Chunlin ZHAO ¹ ⁴, Jie WANG ¹, Xiaoxiao SHU ¹ ⁴, Jiang CHANG ⁵, Jianping JIANG 江建平 ¹ ³, Feng XIE 谢锋 ¹ ³
¹ CAS Key Laboratory of Mountain Ecological Restoration and Bioresource Utilization & Ecological Restoration Biodiversity Conservation Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan, China
中国 四川 成都 中国科学院山地生态恢复与生物资源利用重点实验室 中国科学院成都生物研究所
² Yibin University, Yibin 644000, Sichuan, China
中国 四川 宜宾 宜宾学院
³ University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学
⁴ Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, Sichuan, China
中国 四川 成都 四川大学
⁵ State Key Laboratory of Environmental Criteria and Risk Assessment, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, Beijing 100012, China
中国 北京 中国环境科学研究院环境基准与风险评估国家重点实验室
Asian Herpetological Research
, 2021-09-25
Abstract
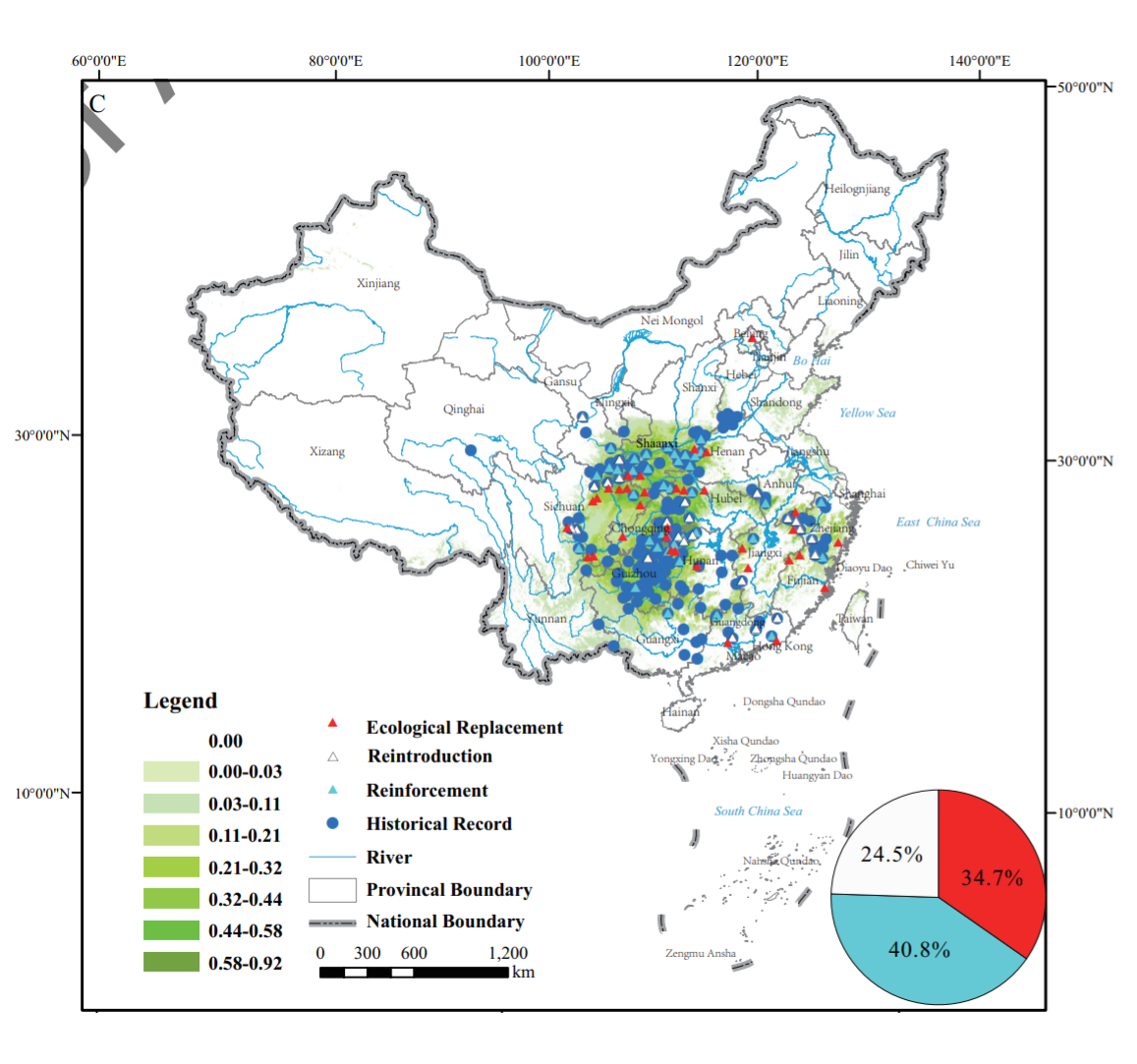
Biodiversity is declining globally by an unprecedented extinction rate. This is especially true for amphibians, accounting for 24.3% of all threatened vertebrates. As the largest extant amphibian species in the world, wild populations of the Chinese giant salamander (Genus Andrias) (CGS) have decreased dramatically because of overexploitation and habitat degradation. Translocation has become an important strategy for restoring threatened wild populations worldwide.
However, disordered translocation usually has negative effects on the native populations. We provide an overview of CGS translocation and show that disordered translocation can increase local population extinction. Nearly four times the estimated number of wild individuals have been released across China. There are three types of translocation used for CGS, namely, reinforcement, reintroduction and ecological replacement, the last of which accounts for over one-third of translocations. Our genetic screening revealed that most released individuals were not from local populations, with one to four lineages detected in every release site (n = 6).
This disordered translocation can potentially reduce the genetic integrity of original populations. Hence, we suggest suspending current CGS translocation activities immediately, until more robust measures can be developed and implemented to improve the current translocation program, especially with respect to lineage identification and the identification of appropriate release sites.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25