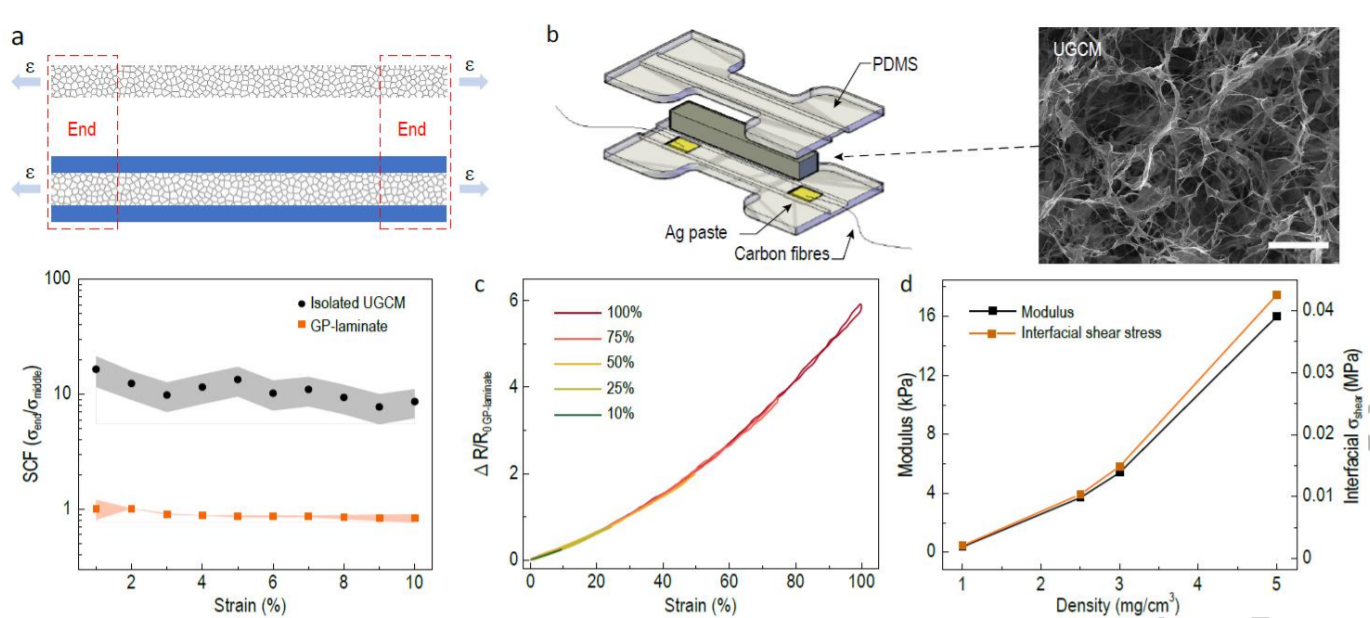
(Peer-Reviewed) Detecting subtle yet fast skeletal muscle contractions with ultrasoft and durable graphene-based cellular materials
Zijun He ¹ ², Zheng Qi ³, Huichao Liu ⁴, Kangyan Wang ¹, Leslie Roberts ⁵ ⁶, Jefferson Z Liu ⁷, Yilun Liu 刘益伦 ⁴, Stephen J Wang 王佳 ⁸ ⁹, Mark J Cook ⁶, George P Simon ², Ling Qiu 丘陵 ² ¹⁰, Dan Li 李丹 ¹ ²
¹ Department of Chemical Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne 3010, Australia
² Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Monash University, Melbourne 3800, Australia
³ Department of Chemical Engineering, Monash University, Melbourne 3800, Australia
⁴ State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures, School of Aerospace Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049 China
中国 西安 西安交通大学航天航空学院 机械结构强度与振动国家重点实验室
⁵ Neurophysiology Department, Department of Neurology & Neurological Research, St Vincent's Hospital, Melbourne 3065, Australia
⁶ 6Department of Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, University of Melbourne, Melbourne 3010, Australia
⁷ Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Melbourne, Melbourne 3010, Australia
⁸ Department of Design, Monash University, Melbourne 3145, Australia
⁹ School of Design, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
中国 香港 香港理工大学设计学院
¹⁰ Shenzhen Geim Graphene Center, Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, China
中国 深圳 清华-伯克利深圳学院 深圳盖姆石墨烯中心
National Science Review
, 2021-10-05