(Peer-Reviewed) Validation and invalidation of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors using the Flip-GFP and Protease-Glo luciferase assays
Chunlong Ma, Haozhou Tan, Juliana Choza, Yuying Wang, Jun Wang 王俊
Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, College of Pharmacy, the University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021-11-01
Abstract
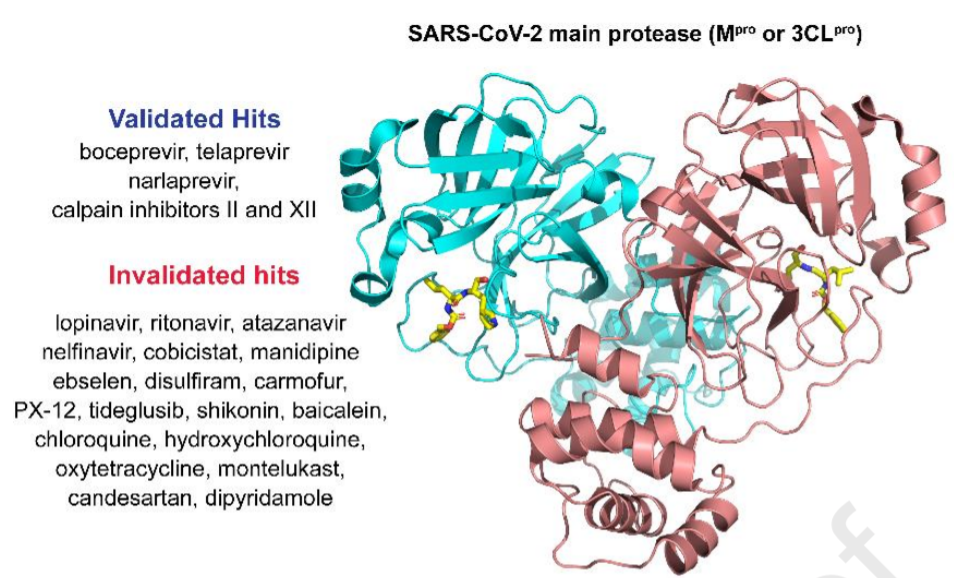
SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mᵖʳᵒ) is one of the most extensively exploited drug targets for COVID-19. Structurally disparate compounds have been reported as Mᵖʳᵒ inhibitors, raising the question of their target specificity. To elucidate the target specificity and the cellular target engagement of the claimed Mᵖʳᵒ inhibitors, we systematically characterize their mechanism of action using the cell-free FRET assay, the thermal shift-binding assay, the cell lysate Protease-Glo luciferase assay, and the cell-based FlipGFP assay.
Collectively, our results have shown that majority of the Mᵖʳᵒ inhibitors identified from drug repurposing including ebselen, carmofur, disulfiram, and shikonin are promiscuous cysteine inhibitors that are not specific to Mᵖʳᵒ, while chloroquine, oxytetracycline, montelukast, candesartan, and dipyridamole do not inhibit Mᵖʳᵒ in any of the assays tested. Overall, our study highlights the need of stringent hit validation at the early stage of drug discovery.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25