(Peer-Reviewed) STI PCR: An efficient method for amplification and de novo synthesis of long DNA sequences
Zhe Zhao 赵哲 ¹ ², Xianrong Xie 谢先荣 ¹ ², Weizhi Liu 刘伟智 ¹ ², Jingjing Huang ¹ ², Jiantao Tan 谭健韬 ¹ ², Haixin Yu ¹ ², Wubei Zong 宗伍辈 ¹ ², Jintao Tang 汤金涛 ¹ ², Yanchang Zhao ¹ ², Yang Xue ¹ ², Zhizhan Chu 初志战 ¹ ², Letian Chen 陈乐天 ¹ ², Yao-Guang Liu 刘耀光 ¹ ²
¹ State Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Subtropical Agro-Bioresources, College of Life Sciences, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou510642, China
中国 广州 华南农业大学生命科学学院 亚热带农业生物资源保护与利用国家重点实验室
² Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture, Guangzhou 510642, China
中国 广州 岭南现代农业科学与技术广东省实验室
Abstract
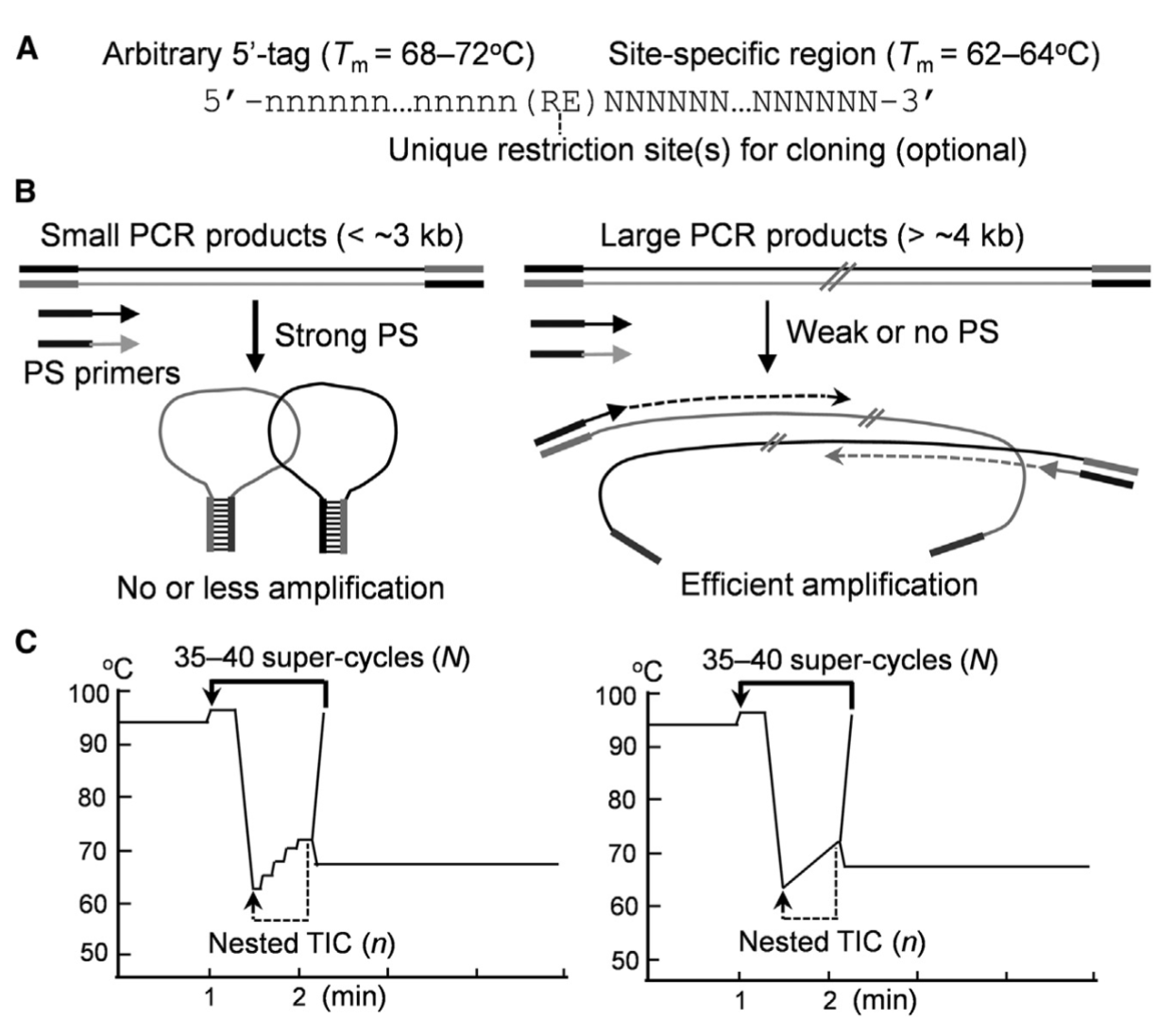
Despite continuous improvements, it is difficult to efficiently amplify large sequences from complex templates using current PCR methods. Here, we developed a suppression thermo-interlaced (STI) PCR method for the efficient and specific amplification of long DNA sequences from genomes and synthetic DNA pools.
This method uses site-specific primers containing a common 5′ tag to generate a stem-loop structure, thereby repressing the amplification of smaller non-specific products through PCR suppression (PS). However, large target products are less affected by PS and show enhanced amplification when the competitive amplification of non-specific products is suppressed. Furthermore, this method uses nested thermo-interlaced cycling with varied temperatures to optimize strand extension of long sequences with an uneven GC distribution. The combination of these two factors in STI PCR produces a multiplier effect, markedly increasing specificity and amplification capacity.
We also developed a webtool, calGC, for analyzing the GC distribution of target DNA sequences and selecting suitable thermo-cycling programs for STI PCR. Using this method, we stably amplified very long genomic fragments (up to 38 kb) from plants and human and greatly increased the length of de novo DNA synthesis, which has many applications such as cloning, expression, and targeted genomic sequencing. Our method greatly extends PCR capacity and has great potential for use in biological fields.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25